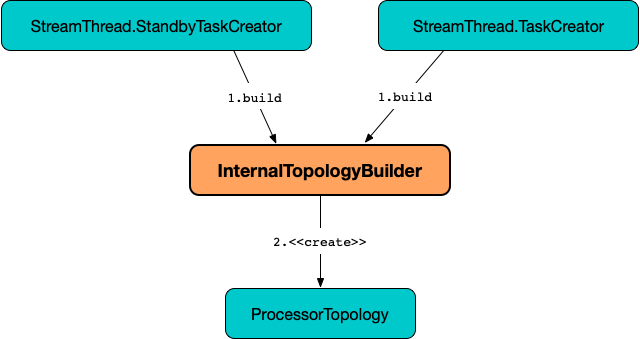
InternalTopologyBuilder
InternalTopologyBuilder is used to build a topology of processor nodes (for StreamThread.StandbyTaskCreator and StreamThread.TaskCreator task factories and hence stream processor tasks themselves).

InternalTopologyBuilder is created exclusively for a Topology (which is simply the frontend to the internals of topology development).
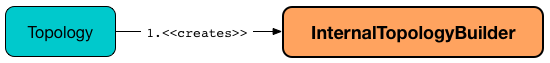
InternalTopologyBuilder takes no arguments when created.
import org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.internals.InternalTopologyBuilder
val builder = new InternalTopologyBuilderInternalTopologyBuilder uses node factories to build a topology. InternalTopologyBuilder supports ProcessorNodeFactory, SourceNodeFactory, and SinkNodeFactory factory types only (and throws a TopologyException for unknown factories).
InternalTopologyBuilder can have one or more sources that are added (registered) using addSource method (which simply registers a SourceNodeFactory under a name).
scala> :type builder
org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.internals.InternalTopologyBuilder
val sourceNodeName = "sourceNode"
import org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.WallclockTimestampExtractor
val timestampExtractor = new WallclockTimestampExtractor
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
val keyDeserializer = new StringDeserializer
val valDeserializer = new StringDeserializer
val topics = Seq("input")
import org.apache.kafka.streams.Topology.AutoOffsetReset
builder.addSource(
AutoOffsetReset.LATEST,
sourceNodeName,
timestampExtractor,
keyDeserializer,
valDeserializer,
topics: _*)InternalTopologyBuilder can have zero or more processor nodes that are added (registered) using addProcessor method (which simply registers a ProcessorNodeFactory under a name with a ProcessorSupplier and one or more predecessors). Since processors require that the predecessors are already added to the topology, a topology has to have at least one source processor already added.
scala> :type builder
org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.internals.InternalTopologyBuilder
assert(!builder.getSourceTopicNames.isEmpty)
val sourceTopicName = "input"
import collection.JavaConverters._
assert(builder.getSourceTopicNames.asScala.contains(sourceTopicName))
import org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.{Processor, ProcessorContext, ProcessorSupplier}
val supplier = new ProcessorSupplier[String, String] {
def get = new Processor[String, String] {
def init(context: ProcessorContext): Unit = {}
def process(key: String, value: String): Unit = {}
def close(): Unit = {}
}
}
val processorNodeName = "processorNode"
val sourceNodeName = "sourceNode"
val predecessorNames = Seq(sourceNodeName)
builder.addProcessor(processorNodeName, supplier, predecessorNames: _*)InternalTopologyBuilder can have zero or more sink nodes that are added (registered) using addSink method (which simply registers a SinkNodeFactory under a name).
scala> :type builder
org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.internals.InternalTopologyBuilder
// FIXME: Finish the demoInternalTopologyBuilder requires an application ID. The application ID is used as a namespace for the internal topics (so they do not clash with the topics of other Kafka Streams applications). The application ID is set using setApplicationId (and is the APPLICATION_ID_CONFIG configuration property that KafkaStreams requires when created).
InternalTopologyBuilder setApplicationId(final String applicationId)InternalTopologyBuilder uses the application id when:
-
buildProcessorNode and topicGroups for the names of changelog topics (when a
StateStoreFactoryhas logging enabled) -
decorateTopic to prefix (decorate) internal topic names
InternalTopologyBuilder has to be optimized using rewriteTopology (that sets the required application ID).
scala> :type builder
org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.internals.InternalTopologyBuilder
import org.apache.kafka.streams.StreamsConfig
import java.util.Properties
val props = new Properties
props.put(StreamsConfig.APPLICATION_ID_CONFIG, "app")
props.put(StreamsConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, ":9092")
val config = new StreamsConfig(props)
builder.rewriteTopology(config)InternalTopologyBuilder can be described (using a TopologyDescription).
scala> :type builder
org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.internals.InternalTopologyBuilder
// add nodes and stores
val description = builder.describe
scala> println(description)
Topologies:
Sub-topology: 0
Source: sourceNode (topics: [input])
--> processorNode
Processor: processorNode (stores: [])
--> none
<-- sourceNodeGlobal Source Node is a node from a SourceNodeFactory with exactly one topic and registered in globalTopics. You can use isGlobalSource predicate to check if a name is of a global source node.
| Name | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
Global state stores by name
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
Names of the internal topics that were auto-created when A new topic name is added when |
||||
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
NodeFactories by node name
|
||||
|
QuickUnion of the names of node groups Used when…FIXME |
||||
|
Node groups by ID, i.e. groups of node names that can be looked up by a group ID ( Initialized when
|
||||
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
Topic names by the source processor node name (without the application ID prefix for internal topics) New entries are added when |
||||
|
Collection of registered topic names Used when…FIXME |
||||
|
StateStoreFactories by name (of the StoreBuilder) (
|
||||
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
Names of the state stores and the names of the corresponding changelog topics (
A new pair is added when |
||||
|
|||||
|
|
||||
|
|
Tip
|
Enable Add the following line to Refer to Application Logging Using log4j. |
Adding Application ID to Topic (As Prefix) — decorateTopic Internal Method
String decorateTopic(final String topic)decorateTopic…FIXME
|
Note
|
|
buildSinkNode Internal Method
void buildSinkNode(
Map<String, ProcessorNode> processorMap,
Map<String, SinkNode> topicSinkMap,
Set<String> repartitionTopics,
SinkNodeFactory sinkNodeFactory,
SinkNode node)buildSinkNode…FIXME
|
Note
|
buildSinkNode is used exclusively when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to build a topology of processor nodes.
|
maybeDecorateInternalSourceTopics Internal Method
List<String> maybeDecorateInternalSourceTopics(final Collection<String> sourceTopics)maybeDecorateInternalSourceTopics…FIXME
|
Note
|
|
resetTopicsPattern Internal Method
Pattern resetTopicsPattern(
final Set<String> resetTopics,
final Set<Pattern> resetPatterns,
final Set<String> otherResetTopics,
final Set<Pattern> otherResetPatterns)resetTopicsPattern…FIXME
|
Note
|
resetTopicsPattern is used when…FIXME
|
copartitionGroups Method
Collection<Set<String>> copartitionGroups()copartitionGroups…FIXME
|
Note
|
copartitionGroups is used exclusively when StreamsPartitionAssignor is requested to perform group assignment (assign tasks to consumer clients).
|
copartitionSources Method
void copartitionSources(
Collection<String> sourceNodes)copartitionSources…FIXME
|
Note
|
copartitionSources is used exclusively when AbstractStream is requested to ensureJoinableWith.
|
Adding Processor to Topology — addProcessor Method
void addProcessor(
String name,
ProcessorSupplier supplier,
String... predecessorNames)addProcessor simply registers a new ProcessorNodeFactory by the given name in the nodeFactories internal registry.
addProcessor also adds the name to the nodeGrouper and unites the processor name with the predecessors.
In the end, addProcessor resets the nodeGroups collection (i.e. null).
|
Note
|
A processor has a unique name, a ProcessorSupplier and at least one predecessor (that cannot be itself) |
addProcessor requires that the given name, the ProcessorSupplier and the predecessor names are all defined (i.e. not null) or throws a NullPointerException.
addProcessor requires that the given name is unique across all the registered nodeFactories or throws a TopologyException.
addProcessor requires that there is at least one predecessor name given or throws a TopologyException.
|
Note
|
|
buildProcessorNode Internal Method
void buildProcessorNode(
Map<String, ProcessorNode> processorMap,
Map<String, StateStore> stateStoreMap,
ProcessorNodeFactory factory,
ProcessorNode node)buildProcessorNode…FIXME
|
Note
|
buildProcessorNode is used exclusively when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to build a topology of processor nodes.
|
buildSourceNode Internal Method
void buildSourceNode(
Map<String, SourceNode> topicSourceMap,
Set<String> repartitionTopics,
SourceNodeFactory sourceNodeFactory,
SourceNode node)buildSourceNode…FIXME
|
Note
|
buildSourceNode is used exclusively when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to build a topology of processor nodes.
|
Adding Source Node to Topology — addSource Method
void addSource(
Topology.AutoOffsetReset offsetReset,
String name,
TimestampExtractor timestampExtractor,
Deserializer keyDeserializer,
Deserializer valDeserializer,
Pattern topicPattern)
void addSource(
Topology.AutoOffsetReset offsetReset,
String name,
TimestampExtractor timestampExtractor,
Deserializer keyDeserializer,
Deserializer valDeserializer,
String... topics)addSource simply registers a new SourceNodeFactory by the given name in the nodeFactories internal registry.
addSource maybeAddToResetList every topic in the given topics.
addSource adds few inputs to the following internal registries:
-
Topics to sourceTopicNames
-
Name with the topics to nodeToSourceTopics
-
Name to nodeGrouper
In the end, addSource resets the nodeGroups collection (i.e. null).
|
Note
|
A source processor has a unique name, a Topology.AutoOffsetReset, a TimestampExtractor, key and value deserializers, a ProcessorSupplier and at least one topic. |
addSource requires that:
-
There is at least one topic or throws a
TopologyException -
Name is specified (not
null) and unique across all the registered nodeFactories or throws aTopologyException -
No topic has been registered earlier
|
Note
|
|
maybeAddToResetList Internal Method
void maybeAddToResetList(
final Collection<T> earliestResets,
final Collection<T> latestResets,
final Topology.AutoOffsetReset offsetReset,
final T item)maybeAddToResetList…FIXME
|
Note
|
maybeAddToResetList is used when…FIXME
|
validateTopicNotAlreadyRegistered Internal Method
void validateTopicNotAlreadyRegistered(final String topic)validateTopicNotAlreadyRegistered…FIXME
|
Note
|
validateTopicNotAlreadyRegistered is used when…FIXME
|
Connecting Processor with State Stores — connectProcessorAndStateStores Method
void connectProcessorAndStateStores(
String processorName,
String... stateStoreNames)connectProcessorAndStateStores simply connectProcessorAndStateStore with processorName and every state store name in stateStoreNames.
connectProcessorAndStateStores reports a NullPointerException when processorName, stateStoreNames or any state store name are nulls.
connectProcessorAndStateStores reports a TopologyException when stateStoreNames is an empty collection.
|
Note
|
connectProcessorAndStateStores (plural) is a public method that uses the internal connectProcessorAndStateStore (singular) for a "bulk connect".
|
|
Note
|
|
Adding Global State Store to Topology — addGlobalStore Method
void addGlobalStore(
StoreBuilder storeBuilder,
String sourceName,
TimestampExtractor timestampExtractor,
Deserializer keyDeserializer,
Deserializer valueDeserializer,
String topic,
String processorName,
ProcessorSupplier stateUpdateSupplier)addGlobalStore first validateGlobalStoreArguments followed by validateTopicNotAlreadyRegistered.
addGlobalStore creates a ProcessorNodeFactory with the given processorName, sourceName (as predecessors) and stateUpdateSupplier (as supplier).
addGlobalStore then does the following housekeeping tasks:
-
Adds the given
topicto globalTopics internal registry -
Creates a SourceNodeFactory and registers it in nodeFactories internal registry as
sourceName -
Associates the
sourceNamewithtopicto nodeToSourceTopics -
Requests QuickUnion of the names of node groups to add the
sourceName -
Requests
ProcessorNodeFactoryto add a state store asname -
Associates the
processorNamewithnodeFactoryin nodeFactories -
Requests QuickUnion of the names of node groups to add the
processorName -
Requests QuickUnion of the names of node groups to unite the
processorNameandpredecessors -
Associates the
namewith thestorein globalStateStores
In the end, addGlobalStore associates the names of the state store and the topic (with the name and topic).
|
Note
|
|
Validating Arguments for Creating Global State Store — validateGlobalStoreArguments Internal Method
void validateGlobalStoreArguments(
final String sourceName,
final String topic,
final String processorName,
final ProcessorSupplier stateUpdateSupplier,
final String storeName,
final boolean loggingEnabled)validateGlobalStoreArguments validates the input parameters (before adding a global state store to a topology).
validateGlobalStoreArguments throws a NullPointerException when sourceName, topic, stateUpdateSupplier or processorName are null.
validateGlobalStoreArguments throws a TopologyException when:
-
nodeFactories contains
sourceNameorprocessorName -
storeNameis already registered in stateFactories or globalStateStores -
loggingEnabledis enabled (i.e.true) -
sourceNameandprocessorNameare equal
|
Note
|
validateGlobalStoreArguments is used exclusively when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to add a global state store to a topology.
|
Registering State Store with Topic (Associating Names) — connectSourceStoreAndTopic Method
void connectSourceStoreAndTopic(
String sourceStoreName,
String topic)connectSourceStoreAndTopic adds the given sourceStoreName with the topic to storeToChangelogTopic internal registry.
connectSourceStoreAndTopic reports a TopologyException when storeToChangelogTopic has sourceStoreName already registered.
Source store [sourceStoreName] is already added.|
Note
|
|
Connecting State Store with Processor Node — connectProcessorAndStateStore Internal Method
void connectProcessorAndStateStore(
String processorName,
String stateStoreName)|
Note
|
connectProcessorAndStateStore (singular) is an internal method that is used by the public connectProcessorAndStateStores (plural).
|
connectProcessorAndStateStore gets the StateStoreFactory for the given stateStoreName (in stateFactories).
connectProcessorAndStateStore then unites all users of the StateStoreFactory with the given processorName. connectProcessorAndStateStore adds the processorName to the users.
connectProcessorAndStateStore gets the NodeFactory for the given processorName (in nodeFactories). Only when the NodeFactory is a ProcessorNodeFactory, connectProcessorAndStateStore registers the stateStoreName with the ProcessorNodeFactory.
In the end, connectProcessorAndStateStore connectStateStoreNameToSourceTopicsOrPattern (with the input stateStoreName and the ProcessorNodeFactory).
connectProcessorAndStateStore reports a TopologyException when the input stateStoreName or processorName have not been registered yet or the processorName is the name of a source or sink node.
|
Note
|
connectProcessorAndStateStore is used when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to add a state store and connect a processor with state stores.
|
connectStateStoreNameToSourceTopicsOrPattern Internal Method
void connectStateStoreNameToSourceTopicsOrPattern(
String stateStoreName,
ProcessorNodeFactory processorNodeFactory)connectStateStoreNameToSourceTopicsOrPattern…FIXME
|
Note
|
connectStateStoreNameToSourceTopicsOrPattern is used exclusively when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to connect a processor with a state store
|
Adding State Store to Topology — addStateStore Method
void addStateStore(
StoreBuilder<?> storeBuilder,
String... processorNames) (1)
void addStateStore(
StoreBuilder<?> storeBuilder,
boolean allowOverride,
String... processorNames)-
Uses
falsefor theallowOverrideflag
addStateStore creates a StateStoreFactory (with the StoreBuilder) and registers it (in the stateFactories internal registry).
addStateStore then connects the state store with processors (if they are given).
In the end, addStateStore resets (nullify) the nodeGroups internal registry.
addStateStore throws a TopologyException when the given StoreBuilder has already been registered (in the stateFactories internal registry) and the allowOverride flag is off (false):
StateStore [name] is already added.|
Note
|
|
Topic Groups (TopicsInfos By IDs) — topicGroups Method
Map<Integer, TopicsInfo> topicGroups()topicGroups…FIXME
|
Note
|
topicGroups is used exclusively when StreamsPartitionAssignor is requested to assign.
|
Getting Node Groups by ID — nodeGroups Accessor Method
synchronized Map<Integer, Set<String>> nodeGroups()nodeGroups gives node groups by id.
If node groups by id registry has not been initialized yet, nodeGroups creates the node groups that are the node groups from now on.
|
Note
|
nodeGroups is used when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to build a topology for a topic group ID, globalNodeGroups and topicGroups
|
Building Global Processor Task Topology — buildGlobalStateTopology Method
ProcessorTopology buildGlobalStateTopology()buildGlobalStateTopology globalNodeGroups and builds a processor task topology with the global node groups.
buildGlobalStateTopology returns null if globalNodeGroups is empty.
|
Note
|
buildGlobalStateTopology is used exclusively when KafkaStreams is created.
|
describeGlobalStore Internal Method
void describeGlobalStore(final TopologyDescription description, final Set<String> nodes, int id)describeGlobalStore…FIXME
|
Note
|
describeGlobalStore is used exclusively when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to describe.
|
nodeGroupContainsGlobalSourceNode Internal Method
void nodeGroupContainsGlobalSourceNode(final TopologyDescription description, final Set<String> nodes, int id)nodeGroupContainsGlobalSourceNode…FIXME
|
Note
|
nodeGroupContainsGlobalSourceNode is used exclusively when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to describe.
|
Checking If Node Name Is Of Global Source Node — isGlobalSource Internal Method
boolean isGlobalSource(final String nodeName)isGlobalSource looks up a NodeFactory by the input node name (in the nodeFactories internal registry).
isGlobalSource is positive (i.e. true) when the following all hold:
-
nodeNameis the name of a SourceNodeFactory with exactly one topic -
The single topic is among globalTopics
Otherwise, isGlobalSource is negative (i.e. false).
|
Note
|
isGlobalSource is used when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to describeGlobalStore, globalNodeGroups and nodeGroupContainsGlobalSourceNode.
|
Global Node Groups — globalNodeGroups Internal Method
Set<String> globalNodeGroups()globalNodeGroups gives node groups with at least one global source node.
|
Note
|
globalNodeGroups is used when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to build a processor task topology and global processor task topology.
|
Building Node Groups — makeNodeGroups Internal Method
Map<Integer, Set<String>> makeNodeGroups()makeNodeGroups starts with no node groups and the local counter of node group IDs as 0.
|
Note
|
makeNodeGroups uses Java’s java.util.LinkedHashMap that is Hash table and linked list implementation of the Map interface, with predictable iteration order.
|
makeNodeGroups takes the names of registered source nodes (from the nodeToSourceTopics and nodeToSourcePatterns internal registries).
makeNodeGroups sorts the names of the source nodes in ascending order (per the natural ordering) and putNodeGroupName for every source node name.
|
Note
|
While putNodeGroupName, makeNodeGroups may end up with a new node group ID. After processing all source node names, the node group ID is the last group ID assigned.
|
makeNodeGroups takes the non-source node names (from the nodeFactories internal registry that are not in the nodeToSourceTopics internal registry).
makeNodeGroups does the same group ID assignment as for the source node names, i.e. sorts the names in ascending order and putNodeGroupName for every node name.
In the end, makeNodeGroups returns the node (names) groups by ID.
|
Note
|
makeNodeGroups is used when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to describe a topology, and get node groups.
|
putNodeGroupName Internal Method
int putNodeGroupName(
final String nodeName,
final int nodeGroupId,
final Map<Integer, Set<String>> nodeGroups,
final Map<String, Set<String>> rootToNodeGroup)putNodeGroupName takes the name of a node, the current node group ID, the current node groups and the rootToNodeGroup.
putNodeGroupName requests QuickUnion of the names of node groups for the root node of the input nodeName.
putNodeGroupName gets the node group for the root node from the input rootToNodeGroup and adds the input nodeName to it.
If the root node was not found in the input rootToNodeGroup, putNodeGroupName registers the root node with an empty node group in rootToNodeGroup. putNodeGroupName then registers the empty node group with an incremented node group ID in nodeGroups.
In the end, putNodeGroupName gives the input nodeGroupId or a new node group ID if the root node was not found in the input rootToNodeGroup.
|
Note
|
putNodeGroupName is used exclusively when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to create the node groups.
|
Describing Topology (as TopologyDescription) — describe Method
TopologyDescription describe()describe…FIXME
import org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.internals.InternalTopologyBuilder
val itb = new InternalTopologyBuilder()
// Create a state store builder
import org.apache.kafka.streams.state.Stores
val lruMapSupplier = Stores.lruMap("input-stream", 5)
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Serdes
import org.apache.kafka.streams.state.{KeyValueStore, StoreBuilder}
val storeBuilder = Stores.keyValueStoreBuilder(
lruMapSupplier,
Serdes.Long(),
Serdes.Long()).
withLoggingDisabled
// Add the state store as a global state store
import org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.TimestampExtractor
val timestampExtractor: TimestampExtractor = null
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.LongDeserializer
val keyDeserializer = new LongDeserializer
val valueDeserializer = new LongDeserializer
import org.apache.kafka.streams.kstream.internals.KTableSource
import org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.ProcessorSupplier
import java.lang.{Long => JLong}
val stateUpdateSupplier: ProcessorSupplier[JLong, JLong] = new KTableSource("global-store")
itb.addGlobalStore(
// Required to make the code compile
storeBuilder.asInstanceOf[StoreBuilder[KeyValueStore[_, _]]],
"sourceName",
timestampExtractor,
keyDeserializer,
valueDeserializer,
"global-store-topic",
"processorName",
stateUpdateSupplier)
import org.apache.kafka.streams.TopologyDescription
val td: TopologyDescription = itb.describe
scala> println(td)
Topologies:
Sub-topology: 0 for global store (will not generate tasks)
Source: sourceName (topics: global-store-topic)
--> processorName
Processor: processorName (stores: [input-stream])
--> none
<-- sourceName|
Note
|
describe is used exclusively when Topology is requested to describe.
|
describeSubtopology Internal Method
void describeSubtopology(
TopologyDescription description,
Integer subtopologyId,
Set<String> nodeNames)describeSubtopology…FIXME
|
Note
|
describeSubtopology is used exclusively when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to describe itself.
|
describeGlobalStore Internal Method
void describeGlobalStore(
final TopologyDescription description,
final Set<String> nodes, int id)describeGlobalStore…FIXME
|
Note
|
describeGlobalStore is used exclusively when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to describe itself.
|
Adding Sink Node to Topology — addSink Method
void addSink(
String name,
String topic,
Serializer<K> keySerializer,
Serializer<V> valSerializer,
StreamPartitioner<? super K, ? super V> partitioner,
String... predecessorNames) (1)
void addSink(
String name,
TopicNameExtractor<K, V> topicExtractor,
Serializer<K> keySerializer,
Serializer<V> valSerializer,
StreamPartitioner<? super K, ? super V> partitioner,
String... predecessorNames)addSink creates a SinkNodeFactory (passing all the inputs along) and registers (adds) it in the nodeFactories internal registry (under the input name).
addSink registers the input topic with the input name in the nodeToSinkTopic internal registry.
addSink adds the input name to the nodeGrouper internal registry and requests it to unite the input name with the input predecessorNames.
|
Note
|
|
Adding Internal Topic Name — addInternalTopic Method
void addInternalTopic(
String topicName)addInternalTopic simply adds the input topicName to the internalTopicNames internal registry.
|
Note
|
|
Building Topology of Processor Nodes — build Method
ProcessorTopology build() (1)
ProcessorTopology build(
Integer topicGroupId) (2)
// PRIVATE
private ProcessorTopology build(
Set<String> nodeGroup)-
Uses build with an undefined
topicGroupId(i.e.null) -
Uses
buildwithnodeGroupbeing the node names for a giventopicGroupId
The private build takes the NodeFactories (from the nodeFactories internal registry).
For every NodeFactory the private build checks if the node (by its name) is included in the input nodeGroup (with the assumption that it is when the nodeGroup is null which can happen when a group ID could not be found in the nodeGroups internal registry) and, if it is, does the following:
-
Requests the
NodeFactoryto build a processor node (and adds it to a localprocessorMapof processors by their names) -
For ProcessorNodeFactories,
buildbuildProcessorNode -
For SourceNodeFactories,
buildbuildSourceNode -
For SinkNodeFactories,
buildbuildSinkNode
In the end, build creates a ProcessorTopology.
build throws a TopologyException for unknown NodeFactories.
Unknown definition class: [className]|
Note
|
nodeGroup can be either global node groups (aka global state topology), a single or all node groups.
|
|
Note
|
The private build is used when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to build a processor task topology (for a group ID) and build a global processor task topology.
|
|
Note
|
The no-argument build is used exclusively when KafkaStreams is created (as a sanity check to fail-fast in case a ProcessorTopology could not be built due to some exception).
|
Building Processor Task Topology For Group ID — build Factory Method
ProcessorTopology build(
Integer topicGroupId)This variant of build takes either a group ID or null (see the parameter-less build()).
For the input topicGroupId specified (i.e. non-null), build looks up the group ID in the nodeGroups internal registry and builds the topology (for the node names in the node group).
When the input topicGroupId is undefined (i.e. null), build takes the node names (from the nodeGroups internal registry) and removes globalNodeGroups. In the end, build builds the topology (for the node names).
|
Note
|
|
allStateStoreName Method
Set<String> allStateStoreName()allStateStoreName simply returns the state store names (the keys) from the stateFactories and globalStateStores internal registries.
|
Note
|
allStateStoreName is used exclusively when TopologyTestDriver is requested to getAllStateStores.
|
Creating InternalTopicConfig (Given Name and StateStoreFactory) — createChangelogTopicConfig Internal Method
InternalTopicConfig createChangelogTopicConfig(
StateStoreFactory factory,
String name)createChangelogTopicConfig creates a UnwindowedChangelogTopicConfig or a WindowedChangelogTopicConfig per the isWindowStore flag of the input StateStoreFactory.
Internally, createChangelogTopicConfig requests the input StateStoreFactory for isWindowStore flag.
|
Note
|
isWindowStore flag is enabled when a StateStoreFactory is created for a WindowStoreBuilder.
|
If isWindowStore flag is enabled (true), createChangelogTopicConfig does the following:
-
Requests the input
StateStoreFactoryfor logConfig and uses it to create a WindowedChangelogTopicConfig (for the inputname) -
Requests the input
StateStoreFactoryfor retentionPeriod and uses it to requests theWindowedChangelogTopicConfigto setRetentionMs
If isWindowStore flag is disabled (false), createChangelogTopicConfig requests the input StateStoreFactory for logConfig and uses it to create a UnwindowedChangelogTopicConfig (for the input name).
|
Note
|
createChangelogTopicConfig is used exclusively when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested for topic groups.
|
Source Topics — sourceTopicPattern Method
Pattern sourceTopicPattern()sourceTopicPattern returns the cached source topics pattern if available.
If not, sourceTopicPattern takes the subscribed topics from the nodeToSourceTopics internal registry and sorts them into ascending order (using natural ordering).
Before returning the source topics pattern, sourceTopicPattern buildPatternForOffsetResetTopics and saves the result in the topicPattern internal registry.
|
Note
|
|
buildPatternForOffsetResetTopics Internal Method
Pattern buildPatternForOffsetResetTopics(
Collection<String> sourceTopics,
Collection<Pattern> sourcePatterns)buildPatternForOffsetResetTopics…FIXME
|
Note
|
buildPatternForOffsetResetTopics is used when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to resetTopicsPattern and sourceTopicPattern.
|
setRegexMatchedTopicsToSourceNodes Internal Method
void setRegexMatchedTopicsToSourceNodes()setRegexMatchedTopicsToSourceNodes…FIXME
|
Note
|
setRegexMatchedTopicsToSourceNodes is used exclusively when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to updateSubscriptions.
|
updateSubscriptions Method
void updateSubscriptions(
final SubscriptionUpdates subscriptionUpdates,
final String logPrefix)updateSubscriptions…FIXME
|
Note
|
updateSubscriptions is used exclusively when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to updateSubscribedTopics.
|
updateSubscribedTopics Method
void updateSubscribedTopics(final Set<String> topics, final String logPrefix)updateSubscribedTopics…FIXME
|
Note
|
updateSubscribedTopics is used when TaskManager is requested to updateSubscriptionsFromAssignment and updateSubscriptionsFromMetadata.
|
rewriteTopology Method
InternalTopologyBuilder rewriteTopology(final StreamsConfig config)rewriteTopology…FIXME
|
Note
|
rewriteTopology is used exclusively when KafkaStreams is created.
|
adjust Internal Method
void adjust(final StreamsConfig config)adjust…FIXME
|
Note
|
adjust is used exclusively when InternalTopologyBuilder is requested to rewriteTopology.
|