val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("Ingesting Data from Kafka")
conf.set("spark.streaming.ui.retainedBatches", "5")
// Enable Back Pressure
conf.set("spark.streaming.backpressure.enabled", "true")
val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, batchDuration = Seconds(5))
// Enable checkpointing
ssc.checkpoint("_checkpoint")
// You may or may not want to enable some additional DEBUG logging
import org.apache.log4j._
Logger.getLogger("org.apache.spark.streaming.dstream.DStream").setLevel(Level.DEBUG)
Logger.getLogger("org.apache.spark.streaming.dstream.WindowedDStream").setLevel(Level.DEBUG)
Logger.getLogger("org.apache.spark.streaming.DStreamGraph").setLevel(Level.DEBUG)
Logger.getLogger("org.apache.spark.streaming.scheduler.JobGenerator").setLevel(Level.DEBUG)
// Connect to Kafka
import org.apache.spark.streaming.kafka.KafkaUtils
import _root_.kafka.serializer.StringDecoder
val kafkaParams = Map("metadata.broker.list" -> "localhost:9092")
val kafkaTopics = Set("spark-topic")
val messages = KafkaUtils.createDirectStream[String, String, StringDecoder, StringDecoder](ssc, kafkaParams, kafkaTopics)
// print 10 last messages
messages.print()
// start streaming computation
ssc.startIngesting Data from Apache Kafka
Spark Streaming comes with two built-in models of ingesting data from Apache Kafka:
-
Using receivers
There is yet another "middle-ground" approach (so-called unofficial since it is not available by default in Spark Streaming):
-
Kafka Spark Consumer — a high-performance Kafka Consumer for Spark Streaming with support for Apache Kafka 0.10.
Data Ingestion with no Receivers
No-receivers approach supports the two following modes:
-
Streaming mode (using KafkaUtils.createDirectStream) that uses a input dstream that polls for records from Kafka brokers on the driver every batch interval and passes the available topic offsets on to executors for processing.
-
Non-streaming mode (using KafkaUtils.createRDD) which simply creates a KafkaRDD of key-value pairs, i.e.
RDD[(K, V)]from the records in topics in Kafka.
Streaming mode
You create DirectKafkaInputDStream using KafkaUtils.createDirectStream.
|
Note
|
Define the types of keys and values in KafkaUtils.createDirectStream, e.g. KafkaUtils.createDirectStream[String, String, StringDecoder, StringDecoder], so proper decoders are used to decode messages from Kafka.
|
You have to specify metadata.broker.list or bootstrap.servers (in that order of precedence) for your Kafka environment. metadata.broker.list is a comma-separated list of Kafka’s (seed) brokers in the format of <host>:<port>.
|
Note
|
You can start DirectKafkaInputDStream regardless of the status of Kafka brokers as it waits until at least one Kafka broker is available.
|
If zookeeper.connect or group.id parameters are not set, they are added with their values being empty strings.
In this mode, you will only see jobs submitted (in the Jobs tab in web UI) when a message comes in.
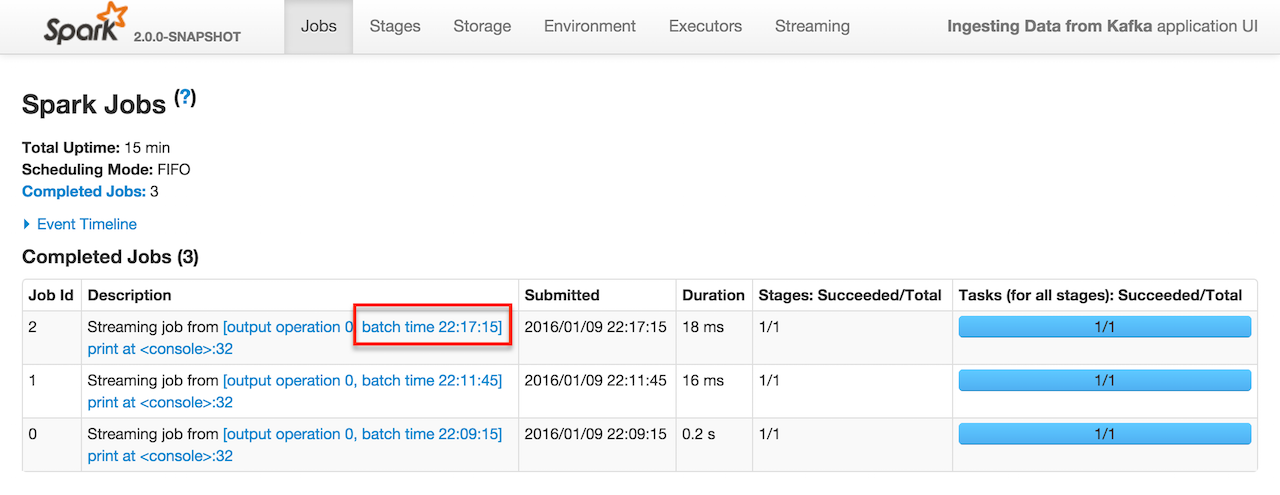
It corresponds to Input size larger than 0 in the Streaming tab in the web UI.

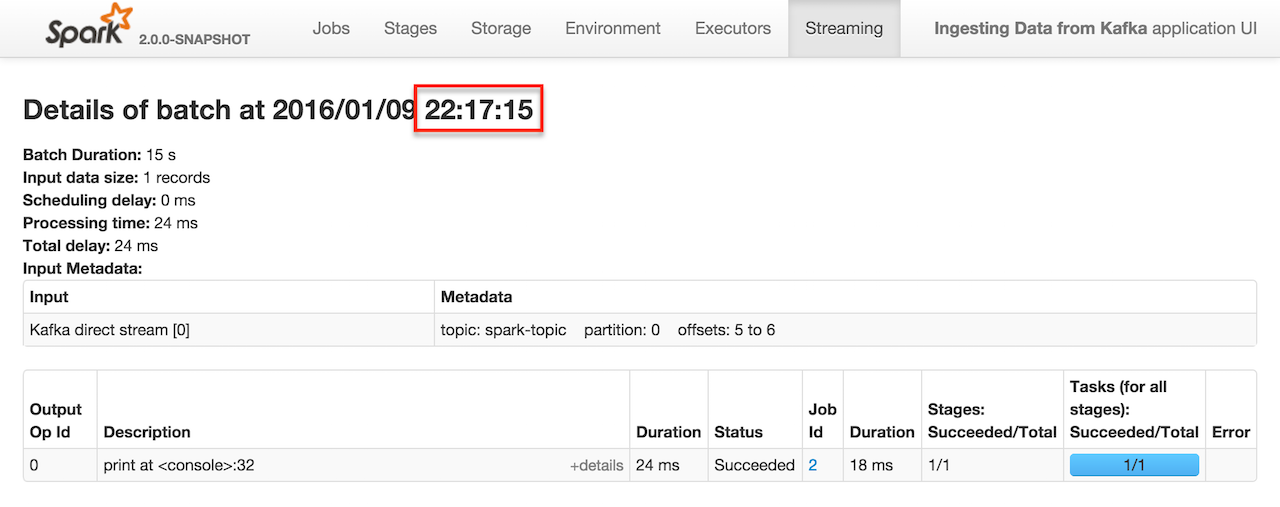
Click the link in Completed Jobs for a batch and you see the details.
spark-streaming-kafka-0-10 Library Dependency
The new API for both Kafka RDD and DStream is in the spark-streaming-kafka artifact. Add the following dependency to sbt project to use the streaming integration:
libraryDependencies += "org.apache.spark" %% "spark-streaming-kafka-0-10" % "2.0.1"|
Tip
|
|
|
Note
|
Replace 2.0.1 or 2.1.0-SNAPSHOT with available version as found at The Central Repository’s search.
|
LeaderOffset
LeaderOffset is an internal class to represent an offset on the topic partition on the broker that works on a host and a port.